Peer Reviewed Articles for Ocupational Therapy Treatments for Major Depressive Disorder
INTRODUCTION
Depression is a mutual psychiatric disorder and a major contributor to the global burden of diseases. According to the Earth Health System, low is the second-leading cause of disability in the world and is projected to rank first past 2030[ane]. Depression is besides associated with high rates of suicidal behavior and mortality[ii].
Treatments administered during the acute phase of a major depressive episode aim to assistance the patient reach a remission state and somewhen return to their baseline level of operation[three]. Acute-phase handling options include pharmacotherapy, depression-focused psychotherapy, combinations of medications and psychotherapy, and somatic therapies such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Notwithstanding, managing the acute phase of depression is merely the outset footstep in a long therapy process that aims to maintain remission and prevent relapses. In this article, we discuss various treatment options implemented by clinicians, highlighting the office that each option plays in actual psychiatric practice.
PHARMACOTHERAPY
While selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) remain the gold-standard treatment for depression, new antidepressants are ever being adult and tested. The ultimate goal is to detect a molecule that exhibits quick effectiveness with as few side effects as possible.
Daniel Bovet studied the structure of histamine (the causative amanuensis in allergic responses) to find an antagonist, which was finally synthesized in 1937[4]. Since then, many researchers have studied the link between the structures and activities of different antihistaminic agents, contributing to the discovery of almost all antidepressants[five].
In the following subsections, we list the main classes of antidepressants in chronological order of apparition, highlighting the nigh widely used molecules in daily psychiatric practice.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Iproniazid was the first drug defined as an antidepressant; information technology was afterward classified as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)[6,7]. Several other MAOIs have been introduced since 1957[8]. Due to their irreversible inhibition of monoamine oxidase, MOAIs take numerous side effects, such as hepatotoxicity and hypertensive crises, that can lead to lethal intracranial hemorrhages. Consequently, MAOIs have become less commonly used over time[9].
Trials have demonstrated that MAOIs' efficacy is comparable to that of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)[ten,11]. However, considering MAOIs' drug interactions, dietary restrictions, and potentially dangerous side effects, they are now about exclusively prescribed for patients who have not responded to several other pharmacotherapies, including TCAs[9]. Furthermore, MAOIs take demonstrated specific efficacy in treating depression with atypical features, such as reactive moods, contrary neuro-vegetative symptoms, and sensitivity to rejection[12].
MAOIs are too a potential therapeutic option when ECT is contraindicated[13]. MAOIs' effectiveness is yet unclear for treating depression in patients who are resistant to multiple sequential trials with SSRIs and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)[14]. Still, psychiatrists' use of MAOIs has declined over the years[15,16]. The use of MAOIs is mostly restricted to patients who practice non reply to other treatments.
TCAs
The first TCA was discovered and released for clinical utilize in 1957 under the brand name Tofranil[5,17]. Since and so, TCAs take remained among the most frequently prescribed drugs worldwide[9]. TCAs-such as amitriptyline, nortriptyline, protrip
However, some TCAs can be more effective than SSRIs when used to treat hospitalized patients[20]. This efficacy can be explained by the superiority of TCAs over SSRIs for patients with severe major depressive disorder (MDD) symptoms who require hospitalization[21-24]. However, no differences have been detected in outpatients who are considered less severely sick[18,20]. In most cases, TCAs should generally be reserved for situations when start-line drug treatments have failed[25].
SSRIs
In December 1987, a serial of clinical studies confirmed that an SSRI called fluoxetine was as effective every bit TCAs for treating depression while causing fewer adverse effects[26]. Subsequently beingness released onto the market place, its employ expanded more than quickly than that of any other psychotropic in history. In 1994, it was the 2nd-best-selling drug in the world[7].
Currently available SSRIs include fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine, fluvoxamine, citalopram, and escitalopram. They take elicited different tolerance rates and side furnishings-mostly sexual and digestive (nausea and loss of ambition), too equally irritability, anxiety, indisposition, and headaches[27]. Nevertheless, SSRIs have a good tolerability profile[28].
In nearly systematic reviews and meta-analyses, SSRIs have demonstrated comparable efficacy to TCAs[18,xix,29], and there is no meaning evidence indicating the superiority of any other class or amanuensis over SSRIs[29-31]. Furthermore, studies show no differences in efficacy among individual SSRIs[29,31-34]. Therefore, near guidelines currently recommend SSRIs every bit the first-line treatment for patients with major depression[25].
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
Other monoamine (norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine) neurotransmitter reuptake inhibitors called SNRIs emerged during the 1990s to protect patients confronting the adverse furnishings of SSRIs[35]. Currently available SNRIs are venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine (the principal metabolite of venlafaxine), and duloxetine. The extended-release form of venlafaxine is the most commonly used drug in this grade. Clinical guidelines ordinarily recommend prescribing SNRI to patients who exercise not answer to SSRIs[25].
In individual studies, venlafaxine and duloxetine are generally considered constructive as SSRIs[36]. Also, venlafaxine's efficacy is comparable to that of TCAs[37,38].
According to some meta-analyses, reboxetine (a selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor) seems less efficacious than SSRIs[39]. Even so, these findings could be due to the relatively poor tolerance of reboxetine[40].
Other antidepressants
Trazodone is the oldest medication of the so-called "other antidepressants" grouping that is still in wide employ[41,42]. It has been shown to exist an effective antidepressant in placebo-controlled research. Yet, in contemporary practise, information technology is much more likely to exist used in low doses as a allaying-hypnotic than equally an antidepressant[41,42].
Nefazodone's structure is analogous to that of trazodone, though information technology has different pharmacological properties[43]. Its efficacy and overall tolerability are comparable to those of SSRIs, as indicated by comparative trials[43]. However, its employ is associated with rare (but fatal) cases of clinical idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity[44].
Bupropion's mechanism of action remains unclear, though it is classified as a norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor[45]. Information technology appears to have a more activating profile than SSRIs that are modestly superior to bupropion in patients with MDD[46]. However, for individuals with low to moderate levels of anxiety, the efficacy of bupropion in treating MDD is comparable to that of SSRIs[46]. Moreover, bupropion has a better tolerability profile than SSRIs, with minimal weight gain (or even leading to weight loss)[46]. In add-on, bupropion is more likely than some SSRIs to ameliorate symptoms of fatigue and sleepiness[47].
Mirtazapine and mianserin are tetracyclic compounds believed to increment the availability of serotonin or norepinephrine (or both), at least initially. Mirtazapine's power to antagonize serotoninergic subtypes receptors, <5-HT2A> and <5-HT2C>, could also increase norepinephrine and dopamine release in cortical regions[25]. Mirtazapine is about as constructive equally SSRIs[48].
Recently, drugs have been developed that block serotonin reuptake while affecting a variety of 5-HT receptor subtypes. The advantages of these agents (eastward.one thousand., vilazodone and vortioxetine) over SSRIs are not fully clear. However, they appear to produce less sexual dysfunction and, in the specific example of vortioxetine, have particular benefits in depression-related cognitive harm[49]. Indeed, vortioxetine is a very contempo antidepressant with a multimodal mechanism that is idea to have a high analogousness for serotonin transporters and 5-HT3, 5HT1A, 5HT7 receptors. Such a specific contour seems to indicate a level of efficacy to other antidepressants with a specific activity on cognitive impairments[50,51].
In conclusion, no pregnant differences accept been institute between different classes of antidepressants in terms of their efficacy[52], though some drugs bear witness some weak-to-moderate prove indicating they are more constructive than another drugs[53]. Concerning the acceptability of these drugs, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline, and vortioxetine have been deemed more tolerable than other antidepressants, whereas amitriptyline, clomipramine, duloxetine, fluvoxamine, trazodone, and venlafaxine had the highest dropout rates[53] because of their more than frequent and severe side furnishings. Nausea and vomiting were the nigh common reasons for treatment discontinuation; sexual dysfunction, sedation, priapism, and cardiotoxicity were besides reported[31,41].
Ketamine and related molecules
In intravenous sub-coldhearted doses, ketamine has very quick effects on resistant unipolar (and, possibly, bipolar) depression and astute suicidal ideation[54,55]. The antidepressant effect of ketamine can persist for several days simply eventually wanes. A few reports are accept cited oral and intranasal formulations of ketamine for handling-resistant depression[56,57], simply there is yet no information near the potential link between the onset of activeness and the road of administration.
Common adverse effects of ketamine include dizziness, neurotoxicity, cognitive dysfunction, blurred vision, psychosis, dissociation, urological dysfunction, restlessness, headache, nausea, airsickness, and cardiovascular symptoms[58]. Such agin effects tend to be brief in acute, depression-dose treatments[36], whereas prolonged exposure may predispose patients to neurotoxicity and drug dependence[56]. Lastly, since ketamine is associated with a college adventure of drug abuse and addiction, it cannot exist recommended in daily clinical practice[59,threescore].
Ketamine is not a miracle drug, and many of import factors still demand to be defined, such as the most effective dose and the optimal assistants route[61,62]. The current lack of guidelines near the therapeutic monitoring of ketamine handling for low farther complicates the expanding use of this treatment[56]. Fifty-fifty though ketamine might never achieve the market, information technology has stimulated research in the neurobiology of low, including studies on potential fast and long-lasting antidepressants.
Ketamine has an agile metabolite (hydroxynorketamine) that can produce rapid and sustained glutamatergic stimulation. It too seems to be free of many of the safety problems associated with ketamine and, thus, should be studied.
Research on the South-enantiomer of ketamine (South-ketamine, or esketamine, especially intranasal) could also be valuable, as it has a 3 to 4 times greater affinity than ketamine for the North-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor[40]. It was approved by the Usa Nutrient and Drug Administration in March 2019 for treatment-resistant depression. Still, current knowledge almost the effects of prolonged esketamine therapy is withal preliminary. In add-on, regarding the potential risk of abuse, esketamine use must be advisedly monitored[63-65].
Other glutamate receptor modulators have been evaluated in pocket-sized studies as monotherapy agents or every bit adjuncts to other antidepressants. Examples include noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists (memantine, dextromethorphan/quinidi-ne, dextromethorphan/bupropion, and lanicemine), NR2B subunit-specific NMDA receptor antagonists (traxoprodil), NMDA receptor glycine site fractional agonists (D-cycloserine, rapastinel), and metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists (basim
Table 1 Principal classes of antidepressants with their engagement of blessing, contributions, and disadvantages.
| Product | Date of FDA1 approval | Contributions | Disadvantages | |
| MAOI two | Iproniazid | 1958 | Confirmed the function of monoaminergic transmission in depression | Drug interactions, dietary restrictions |
| Led to a new search methodologies to develop new antidepressants | Hepatotoxicity and hypertensive crises | |||
| TC 3 | Imipramine | 1959 | Efficacy in patients with more than severe symptoms of MDD | Cardiovascular toxicity and anticholinergic side effects. Risk of lethal toxicity from overdoses |
| Desipramine | ||||
| Nortriptyline | 1992 | |||
| Amitriptyline | 1961 | |||
| Clomipramine | Not approved | |||
| Starting time tetracyclicmaprotiline | ||||
| SSRI 4 | Fluoxetine | 1987 | Improved tolerability | Several minor side effects (sexual dysfunction, loss of appetite, vomiting, nausea, irritability, anxiety, insomnia, and headache). Paroxetine had the highest rate of sexual dysfunction. Fluvoxamine is associated with the about overall adverse events |
| Citalopram | 1998 | |||
| Fluvoxamine | 2007 | |||
| Paroxetine | 1992 | |||
| Escitalopram | 2002 | |||
| Sertraline | 1999 | |||
| SNRI five | Venlafaxine | 2008 | Normally recommended for patients who exercise not answer to SSRIs | No improvement in efficacy. Lower tolerability (highest rates of nausea, vomiting, and sexual dysfunction) |
| Duloxetine | 2004 | |||
| Reboxetine | Non approved | |||
| Other antidepressants | Trazodone | 1981 | Comparable efficacy to SSRIs | High rate of somnolence |
| Nefazodone | 2003 | Rare but fatal hepatotoxicity | ||
| Bupropion | 2003 | A better tolerability profile (minimal weight gain or even weight loss). Likely to improve symptoms of fatigue and sleepiness | May increment risk for seizures (low evidence) | |
| Vortioxetine | 2013 | Efficacy in elderly patients. Supposed cognitive-enhancing properties. Safety contour is similar to SSRIs | The most commonly reported adverse effect was nausea | |
| Vilazodone | 2011 | Less sexual dysfunction (low evidence). Safe profile is similar to SSRIs | The well-nigh unremarkably reported adverse effects were diarrhea and nausea | |
| Mirtazapine | 1997 | Comparable efficacy to SSRIs. Depression hazard of sexual dysfunction | Weight gain | |
| Ketamine and related drugs | Ketamine | Not approved | Rapid effects on resistant depression and acute suicidal ideation | Curt antidepressant effect. Possible neurotoxicity and drug dependence |
| Esketamine | 2019 | Treatment-resistant depression. Greater analogousness for NMDA receptor than ketamine | Potential chance of abuse. Lack of hindsight | |
Perspectives
A purely neurotransmitter-based caption for antidepressant drug action-espe
This finding shows that inquiry on the pharmacological options for treating depression must become beyond monoaminergic neurotransmission systems. Inquiry on the evolution of new antidepressants should explore several mechanisms of action on several types of receptors: Antagonism, inhibition of the reuptake of neurotransmitters, and modulators of glutamate receptors, too equally interactions with α-amino-iii-acid receptors, hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, tyrosine kinase B receptor (the mechanistic target of rapamycin), and glycogen synthase kinase-3[72].
Identifying the cellular targets of rapid-acting agents similar ketamine could help practitioners develop more constructive antidepressant molecules by revealing other receptors involved in gamma-aminobutyric acrid regulation and glutamate trans
PSYCHOTHERAPY
Psychotherapeutic interventions are widely used to treat and foreclose well-nigh psychiatric disorders. Such interventions are mutual in cases of depression, psychosocial difficulties, interpersonal problems, and intra-psychic conflicts. The specific psychotherapy approach chosen for whatever given example depends on the patient's preference, as well as on the clinician'due south background and availability[74]. Psychotherapy for patients with depression strengthens the therapeutic alliance and enables the patient to monitor their mood, meliorate their functioning, empathize their symptoms better, and master the practical tools they need to cope with stressful events[75]. The following subsections briefly draw psychotherapeutic interventions that have been designed specifically for patients with depression.
Overview of psychotherapy in depression
Depression-focused psychotherapy is typically considered the initial treatment method for mild to moderate MDD. Based on significant clinical bear witness, two specific psychotherapeutic methods are recommended: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT). Supportive therapy (ST) and psychoeducational intervention (PEI) have likewise been recommended, those the evidence supporting these methods s not every bit strong. In more than cases of severe depression, ST and PEI are used only to augment pharmacological treatments.
Afterwards remission, CBT, PEI, and mindfulness-based cerebral therapy (MBCT) are proposed to maintain and prevent depression. However, when psychotherapy has been effective during the initial phases of a depressive episode, it should be continued to maintain remission and prevent relapses while reducing the frequency of sessions[25,75,76].
Specific and intensive psychotherapeutic back up is recommended for patients with chronic depression because of loftier rates of comorbidity with personality disorders, early trauma, and attachment deficits. The European Psychiatric Association recommends using the Cerebral Behavioral Assay Organisation of Psychotherapy (CBASP) for treating chronic low and utilizing specific approaches suited to each patient'due south preferences[77]. All these therapeutic options are summarized in Figure 1.
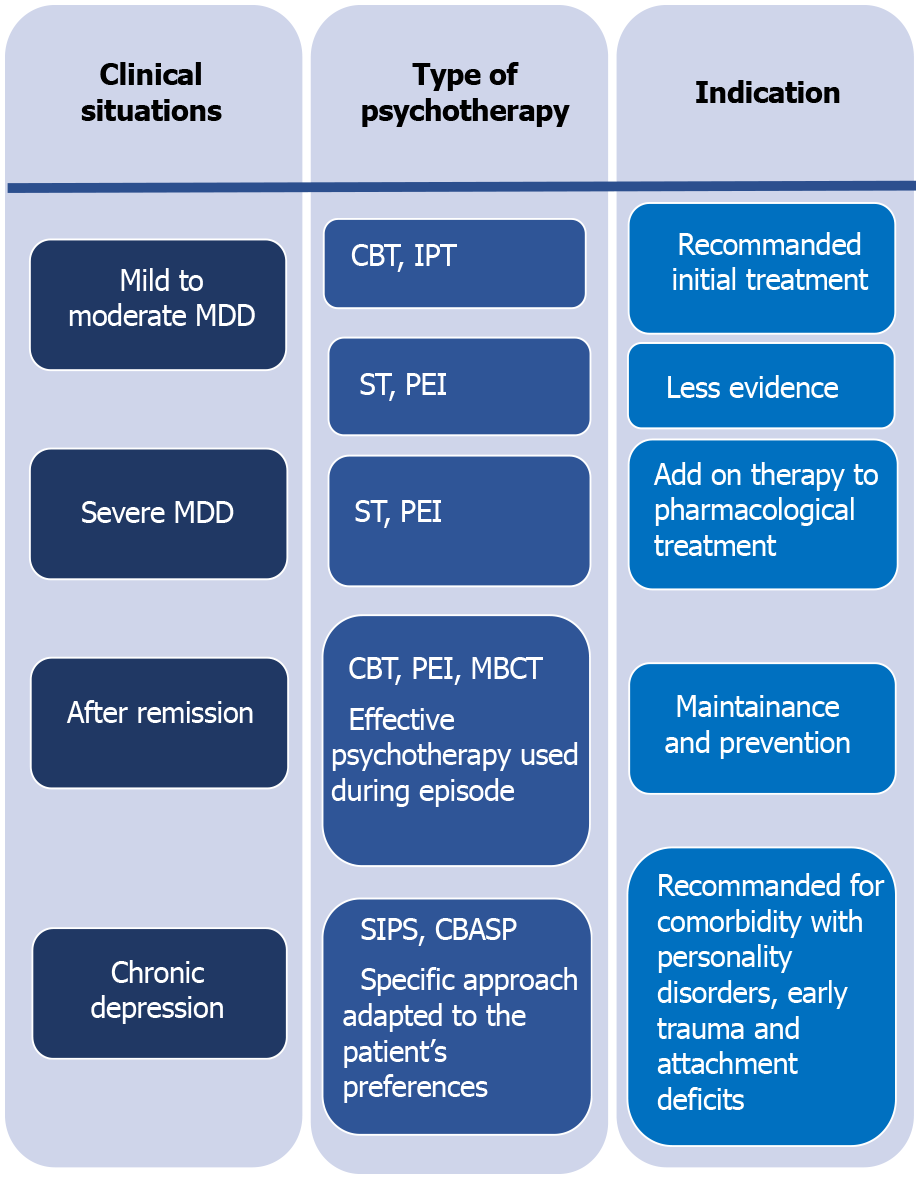
Figure 1Overview of psychotherapy in dissimilar clinical situations of depression. MDD: Major depressive disorder; CBT: Cognitive-behavioral therapy; IPT: Interpersonal therapy; ST: Supportive therapy; PEI: Psycho-educational intervention; MBCT: Mindfulness based cognitive therapy; SIPS: Specific and intensive psychotherapeutic support; CBASP: Cognitive Behavioral Analysis System of Psychotherapy.
Structured psychotherapies
Cognitive and behavioral therapies: Based on robust evidence, CBT is one of the most well-documented and validated psychotherapeutic methods available. Interventional strategies are based on modifying dysfunctional behaviors and cognitions[77]. CBT targets depressed patients' irrational beliefs and distorted cognitions that perpetuate depressive symptoms past challenging and reversing them[three]. Thus, CBT is a well-known constructive treatment method for MDD[78] and has been recommended in most guidelines as a first-line treatment[79-81].
However, the effectiveness of CBT depends on patient's capacity to observe and alter their own beliefs and behaviors. Some simple techniques were developed to overcome this issue, specially in primary intendance direction. Behavioral activation is one such technique, consisting of integrating pleasant activities into daily life to increment the number and intensity of the positive interactions that the patient has with their surround[82,83].
Acceptance and commitment therapy is some other form of CBT. This type of therapy, which is based on functional contextualism, tin aid patients have and adjusting to persistent issues. It appears to be constructive in reducing depressive symptoms and preventing relapses[77,84].
Another form of CBT is computerized CBT (CCBT), implemented via a computer with a CD-ROM, DVD, or online CCBT, allowing patients to benefit from this therapy under atmospheric condition of reduced mobility, remoteness, solitude, or quarantine[79].
CCBT and guided bibliotherapy based on CBT could exist considered for self-motivated patients with balmy to moderate major low or equally a complementary treatment to pharmacotherapy[25]. CBT is besides recommended for patients with resistant depression in combination with antidepressants[85].
Schema therapy is some other CBT-derived therapy that can be used in patients who have failed classical CBT, similar patients with personality disorder comorbidity. Schema therapy is most as constructive as CBT for treating depression[86]. In adolescent patients with depression, CBT is also a recommended option with enough of evidence from multiple trials. Meanwhile, information technology remains the first-line handling in children despite mixed findings across trials[87]. CBT is also a promising option for elderly depressed patients, though substantial evidence is still lacking considering of the limited data on the subject[88].
IPT: The goal of IPT is to identify the triggers of depressive symptoms or episodes. These triggers may include losses, social isolation, or difficulties in social interactions. The role of the intervention is to facilitate mourning (in the case of bereavement), help the patient recognize their own affect, and resolve social interaction dysfunction by building their social skills and social supports[89]. IPT, like CBT, is a start-line treatment for balmy to moderate major depressive episodes in adults; it is too a well-established intervention for adolescents with depression[25].
Problem-solving therapy: The trouble-solving therapy (PST) arroyo combines cognitive and interpersonal elements, focusing on negative assessments of situations and problem-solving strategies. PST has been used in different clinical situations, like preventing depression among the elderly and treating patients with mild depressive symptoms, peculiarly in principal care. Despite its small upshot sizes, PST is comparable to other psychotherapeutic methods used to treat depression[88,90].
Marital and family unit therapy: Marital and family therapy (MFT) is constructive in treating some aspects of low. Family therapy has also been used to treat severe forms of depression associated with medications and hospitalization[91]. Marital and family bug can make people more vulnerable to depression, and MFT addresses these issues[92]. Marital therapy includes both members of the couple, equally low is considered in an interpersonal context in such cases. Some of the goals of this therapy are to facilitate communication and resolve different types of marital conflict. Family therapy uses similar principles every bit other forms of therapy while involving all family members and because depression within the context of pathological family dynamics[93].
ST: Although ST is not likewise-structured or well-evaluated every bit CBT or IPT, it is still commonly used to support depressed patients. In improver to sympathetic listening and expressing concern for the patient'southward problems, ST requires emotionally attuned listening, empathic paraphrasing, explaining the nature of the patient's suffering, and reassuring and encouraging them. These practices permit the patient to ventilate and accept their feelings, increment their self-esteem, and enhance their adaptive coping skills[94].
Psychodynamic therapy: Psychodynamic therapy encompasses a range of cursory to long-term psychological interventions derived from psychoanalytic theories. This type of therapy focuses on intrapsychic conflicts related to shame, repressed impulses, problems in early on childhood with 1's emotional caretakers that lead to low self-esteem and poor emotional self-regulation[93,95]. Psychodynamic therapy's efficacy in the acute phase of MDD is well-established compared to other forms of psychotherapy.
Group therapy: The application of grouping therapy (GT) to MDD remains limited. Some data support the efficacy of specific types of GT inspired by CBT and IPT[96-98]. Group CBT for patients with subthreshold low is an effective postal service-depressive-symptomatology treatment just not during the follow-upward flow[99]. Supportive GT and group CBT reduce depressive symptoms[96], peculiarly in patients with mutual comorbid weather[100]. However, studies are still lacking in this domain.
MBCT: MBCT is a relatively contempo technique that combines elements of CBT with mindfulness-based stress reduction[101]. Studies have shown that eight weeks of MBCT treatment during remission reduces relapse. Thus, it is a potential culling to reduce, or fifty-fifty stop, antidepressant treatment without increasing the risk of depressive recurrence, especially for patients at a high risk of relapse (i.e., patients with more than two previous episodes and patients who have experienced childhood abuse or trauma)[102].
Other psycho-interventions
Psycho-education: This blazon of intervention educates depressed patients and (with their permission) family members involved in the patient's life about depression symptoms and management. This education should exist provided in a language that the patient understands. Issues such as misperceptions about medication, treatment duration, the risk of relapse, and prodromes of depression should be addressed. Moreover, patients should exist encouraged to maintain healthy lifestyles and heighten their social skills to prevent depression and boost their overall mental wellness. Many studies accept highlighted the role of psycho-education in improving the clinical class, treatment adherence, and psychosocial functioning in patients with depression[103].
Physical practice: Well-nigh guidelines for treating depression, including the National Constitute for Health and Care Excellence, the American Psychiatric Association, and the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists, recommend that depressed patients perform regular physical activity to alleviate symptoms and prevent relapses[104]. Exercise also promotes improvements in one's quality of life in full general[105]. However, do is considered an adjunct to other anti-depressive treatments[25].
Although psychotherapy is constructive for treating low and improving patients' quality of life, its direct actions confronting depressive symptoms are not fully understood[106]. Identifying factors (e.g., interpersonal variables) linked to handling responses can assist therapists choose the right therapeutic strategy for each patient and guide research to change existing therapies and develop new ones[107].
Since low is a chief care problematic, simplifying psychotherapy procedures will increment the utilize of psychological interventions for low, peculiarly in general do. Cursory forms (half dozen to eight sessions) of CBT and PST have already shown their effectiveness for treating depression[108]. Even so, simpler solutions must be made available to practitioners to help them manage and prevent depression.
SOMATIC TREATMENTS
In many situations, depression tin can also be managed via somatic treatments. ECT is the most well-known treatment for resistant depression, and solid show supports its effectiveness and rubber. In recent decades, various innovative techniques have been proposed, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), vagus nervus stimulation (VNS), deep encephalon stimulation (DBS), and magnetic seizure therapy, with varying efficiency levels[109].
ECT
ECT is arguably the most constructive treatment modality in psychiatry, and its superiority over pharmacotherapy for major unipolar low is widely supported[110]. ECT reduces the number of hospital readmissions and lightens the burden of depression, leading to a amend quality of life[111,112].
Moreover, ECT is considered safe[113]. Advances in anesthesia and ECT techniques have decreased complications related to ECT while also improving cognitive outcomes and patient satisfaction.
However, the stigma surrounding ECT limits its use. Most misconceptions engagement dorsum to early ECT techniques (when it was performed without muscle relaxants or anesthesia). Nevertheless, some people all the same consider ECT every bit the last selection for treating low, fifty-fifty though about studies indicate that ECT is more beneficial in patients with fewer pharmacological treatments[114-116].
ECT is typically recommended for patients with severe and psychotic depression, a high chance of suicide, or Parkinson's affliction, as well equally pregnant patients[117-119]. The maintenance ECT also appears to prevent relapses[120]. The current do of ECT continues to better equally protocols get more avant-garde, mainly owing to bioinformatics, and as more research is carried out in this domain[121-125].
rTMS
This method, which is a type of biological stimulation that affects brain metabolism and neuronal electrical activity, has been widely used in enquiry on depression[126]. Recent literature shows a significant difference between rTMS and fictitious stimulation regarding its improvements in depressive symptoms[127]. Preliminary research has revealed synergistic (east.g., rTMS/quetiapine) and antagonizing (due east.g., rTMS/cannabinoid receptor (CB1) adversary) interactions between neuro-modulation and pharmacotherapy[128]. Treatments combining rTMS and antidepressants are significantly more than constructive than placebo conditions, with balmy side effects and proficient acceptability[129]. Although these results are encouraging, they remain inconsistent due to differences in rTMS handling frequencies, parameters, and stimulation sites[129]. Therefore, clinical trials with large sample sizes are needed to specify which factors promote favorable therapeutic responses. Also, additional preclinical research should investigate the synergistic effects of other pharmacological molecules and guide integrated approaches (rTMS plus pharmacotherapy).
tDCS
This technique delivers weak currents to the brain via electrodes placed on the scalp[130]. It is easy to use, prophylactic, and tolerable[131]. The tDCS technique significantly outperforms the simulator in terms of the charge per unit of response and remission[132]. However, its effect remains lower than that of antidepressants[133] and rTMS[134]. It can be used as a complementary intervention or as monotherapy to reduce depressive symptoms in unipolar or bipolar depression patients[135]. The antidepressant furnishings of tDCS may involve long-term neuroplastic changes that go along to occur even after the acute phase of treatment, which explains its delayed efficacy[135].
Recently, neurophysiological studies have shown that the clinical effects of tDCS practise non have a direct linear relationship with the dose of stimulation[136]. tDCS, as a relatively elementary and portable technology, is well-suited for remote supervised handling and cess at dwelling house, thus facilitating long treatment durations[136].
Since the optimal clinical effects of tDCS are delayed, hereafter clinical trials should utilize longer evaluation periods and aim to identify responsive patients using algorithms[137].
VNS
VNS is a therapeutic method that has been used for the last sixteen years to treat resistant unilateral or bipolar depression. All the same, despite several clinical studies attesting to its favorable benefit-gamble ratio and its approval by the Food Drug Assistants in 2005, it is not used very often[138].
VNS involves the implantation of a pacemaker nether the collarbone that is connected to an electrode surrounding the left vagus nerve. The left vagus nervus is preferred because it exposes the patient to fewer potential agin cardiac effects. Indeed, almost cardiac afferent fibers originate from the right vagus nerve[139]. Since the plow of the century, numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of VNS in resistant low[140-142].
However, only one randomized, double-bullheaded, controlled trial comparing VNS with usual medical treatment has been conducted over a curt menses of x wk[141]. Moreover, the results of this written report did non signal that the combination of VNS with typical medical treatments was improve than the typical medical treatment on its own.
However, VNS has demonstrated progressively increasing improvements in depressive symptoms, with significant positive outcomes observed later on six to 12 mo; these benefits tin can last for up to two years[143].
More long-term studies are needed to fully determine the predictors of the correct response.
DBS
According to the literature, DBS of the subgenual cingulate white matter (Brodmann surface area = BA 25) elicited a clinical response in sixty% of resistant low patients after six months and clinical remission in 35% of patients, with benefits maintained for over 12 mo[144]. The stimulation of other targets, in particular the nucleus accumbens, to care for resistant depression has gained involvement recently. Behavioral effects indicate the quick and favorable touch on of stimulation on anhedonia, with significant effects on mood appearing as early equally week one after treatment begins[145].
Magnetic seizure therapy
Magnetic seizure therapy involves inducing a therapeutic seizure by applying magnetic stimulation to the brain while the patient is under anesthesia. This technique is still beingness investigated every bit a viable alternative to ECT to treat many psychiatric disorders. Evidence supporting its effectiveness on depressive symptoms continues to grow, and it appears to induce fewer neurocognitive effects than ECT[146,147].
Luxtherapy (phototherapy)
The first description of reduced low symptoms due to intense calorie-free exposure was presented in 1984[148]. Optimal improvements were obtained with vivid lite exposure of 2500 Lux for two hours per day, with forenoon exposure shown to be superior to evening exposure[149].
A review and meta-analysis[150] showed that more intense (but shorter) exposures (10000 Lux for half an 60 minutes per mean solar day or 6000 Lux for one.v h per 24-hour interval) accept the aforementioned efficacy. Chiefly, this treatment method is effective both for those with seasonal and non-seasonal depression. Benefits of phototherapy related to sleep impecuniousness and drug treatments have likewise been reported[151].
Neuro-modulation treatments offer a range of treatment options for patients with depression. ECT remains the almost documented and effective method in this category[151]. rTMS is an interesting technique besides, as it offers a well-tolerated profile[85], while tDCS offers encouraging just varying results that depend on the study's design and the techniques used[130].
More investigations are needed to specify which indications are the best for each method co-ordinate to the clinical and biological profiles of patients. The uses of such methods are expanding, probably, with their efficiency increasing when they are tailored to the patient. Furthermore, somatic interventions for depression need to be regularly assessed and integrated into psychiatrists' therapeutic arsenals.
CONCLUSION
Treating depression is still a significant challenge. Finding the all-time selection for each patient is the best mode to obtaining curt- and long-term effectiveness. The three main methods available to caregivers are antidepressants, specifically structured psychotherapies, and somatic approaches. Research on depression pharmacotherapy continues to examine new molecules implicated in gamma-aminobutyric acid regulation and glutamate manual. Also, efforts to personalize and simplify psychotherapeutic interventions are ongoing. Protocols using somatic interventions need to be studied in more than depth, and their indications must be specified. ECT is the only somatic treatment with confirmed indications for sure forms of low. Combinations of medications, psychotherapy, and somatic therapies remain the nearly constructive means to manage resistant forms of depression.
Source: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i31/9350.htm
Postar um comentário for "Peer Reviewed Articles for Ocupational Therapy Treatments for Major Depressive Disorder"